Introduction:
Understanding hatching time is crucial for bird conservation efforts. The timing of hatching can have significant impacts on bird populations, as it affects the survival and reproductive success of individuals. Hatching time refers to the period between when an egg is laid and when it hatches into a chick. This period is influenced by various factors, including temperature, humidity, nest location, genetics, parental care, environmental factors, egg size and shape, predation, and incubation techniques.
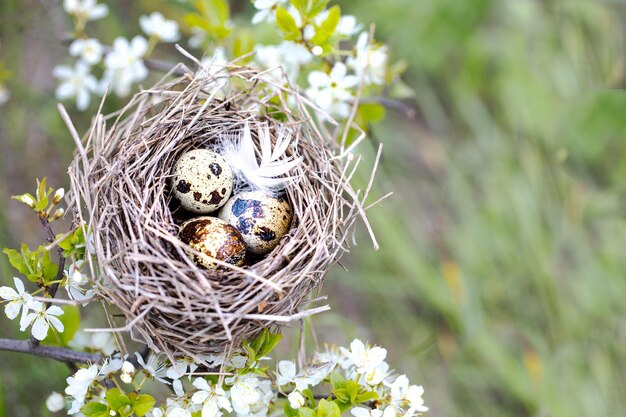

Factors Affecting Incubation Period: Temperature, Humidity, and Nest Location
Temperature plays a vital role in the incubation period of bird eggs. Different bird species have specific temperature requirements for successful incubation. The optimal temperature range allows for proper development of the embryo inside the egg. Deviations from this range can lead to delayed hatching or even death of the embryo. High temperatures can accelerate development and result in premature hatching, while low temperatures can slow down development and prolong the incubation period.
Humidity also affects hatching time. Eggs need a certain level of moisture to maintain their structural integrity and allow gas exchange between the developing embryo and the outside environment. Insufficient humidity can cause dehydration and shrinkage of the egg, leading to developmental abnormalities or death of the embryo. On the other hand, excessive humidity can promote bacterial growth and increase the risk of infection.
Nest location is another factor that influences hatching time. The choice of nest location can impact the temperature and humidity levels experienced by the eggs. Birds often select nest sites that provide optimal conditions for incubation, such as shelter from extreme weather conditions and predators. Nest location can also affect the availability of food resources for the parents during incubation, which indirectly influences hatching time.
The Role of Genetics in Hatching Time: Inherited Traits and Adaptation
Hatching time can be influenced by inherited traits. Some bird species have genetic variations that affect the duration of the incubation period. These variations can be passed down from generation to generation, resulting in consistent hatching time patterns within a population. For example, certain genetic traits may cause eggs to hatch earlier or later than average, depending on the environmental conditions.
Birds also exhibit adaptation to environmental factors that affect hatching time. Natural selection favors individuals with traits that allow them to successfully reproduce in their specific habitats. Birds that have adapted to specific environmental conditions may have shorter or longer incubation periods compared to closely related species. This adaptation ensures that the eggs hatch at the optimal time for chick survival and reproductive success.
Parental Care and Incubation: How Bird Behavior Affects Hatching Time
Parental care plays a crucial role in successful incubation and hatching. Both male and female birds contribute to the incubation process, taking turns to warm the eggs and ensure their proper development. The behavior of the parents during incubation can influence hatching time. For example, if one parent spends less time incubating the eggs than the other, it can result in delayed hatching or uneven development of the embryos.
Bird behavior, such as nest attendance and egg turning, also affects hatching time. Birds need to regularly attend to their nests to maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels for incubation. They may also need to turn the eggs periodically to ensure even heat distribution and prevent the embryos from sticking to the inner shell membrane. Neglecting these behaviors can lead to delayed hatching or developmental abnormalities.
Environmental Factors: Pollution, Habitat Loss, and Climate Change
Environmental factors have significant impacts on hatching time and bird populations. Pollution, such as chemical contaminants in water bodies or air pollution, can affect the quality of eggs and hinder proper development of embryos. Exposure to pollutants can lead to reduced fertility, increased embryo mortality, and developmental abnormalities in hatched chicks.
Habitat loss is another major threat to bird populations and can disrupt the timing of hatching. Destruction of nesting sites and loss of suitable foraging areas can lead to decreased reproductive success and delayed hatching. Birds may struggle to find suitable locations for their nests, resulting in increased vulnerability to predation and exposure to unfavorable environmental conditions.
Climate change is a global phenomenon that is altering the timing of natural events, including hatching time. Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns can disrupt the synchronization between the availability of food resources and the hatching of chicks. If the timing of hatching does not align with the peak abundance of food, it can negatively impact chick survival and overall population health.
Egg Size and Shape: How Physical Characteristics Affect Hatching Time
Egg size and shape can also influence hatching time. Larger eggs generally take longer to hatch compared to smaller eggs. This is because larger eggs contain more nutrients and require more time for the embryo to fully develop. The size of the egg can also affect the rate of heat transfer, which can impact the incubation period.
Egg shape can also play a role in hatching time. Birds that lay elongated or pointed eggs may have shorter incubation periods compared to those that lay rounder eggs. The shape of the egg can affect heat distribution and gas exchange, which can influence the rate of development and ultimately, hatching time.
Predation and Nesting Success: The Impact on Hatching Time and Bird Populations
Predation is a significant factor that affects nesting success and hatching time. Nest predation can result in the destruction of eggs or the death of chicks before they have a chance to hatch. Birds may adjust their hatching time in response to predation pressure, either by delaying or advancing their laying dates. This adaptive response aims to minimize the risk of predation and increase the chances of successful reproduction.
Nesting success, which refers to the proportion of eggs that successfully hatch into chicks, is closely linked to hatching time. If the timing of hatching is not synchronized with the availability of food resources or favorable environmental conditions, it can lead to reduced nesting success. This can have long-term consequences for bird populations, as it affects the number of individuals that survive to reproductive age and contribute to future generations.
Incubation Techniques: Artificial Incubation and Conservation Efforts
Artificial incubation techniques have been developed to aid in bird conservation efforts. In situations where natural incubation is not possible or successful, such as in captive breeding programs or when eggs are at risk of destruction, artificial incubation can be used to ensure the survival of the embryos. This technique involves replicating the optimal temperature and humidity conditions required for successful incubation.
Conservation efforts are crucial for protecting bird species and their hatching time. Habitat restoration, protection of nesting sites, and reduction of pollution are essential steps in ensuring optimal conditions for incubation. Conservation organizations also play a vital role in raising awareness about the importance of hatching time and implementing measures to protect bird populations.
Hatching Synchrony: The Importance of Timing for Chick Survival
Hatching synchrony refers to the phenomenon where eggs within a clutch hatch within a short period of time. This synchrony is important for chick survival, as it ensures that all chicks have an equal chance of receiving parental care and accessing food resources. If hatching is not synchronized, older chicks may outcompete younger ones for food, leading to reduced survival rates.
Hatching synchrony can be influenced by various factors, including genetics, environmental conditions, and parental behavior. Birds may adjust their laying dates or incubation behavior to promote synchrony within a clutch. This adaptation maximizes the chances of chick survival and contributes to the overall health of bird populations.
Conclusion: The Need for Further Research and Conservation Efforts to Protect Bird Species
Understanding hatching time is crucial for bird conservation efforts. The factors that influence hatching time, such as temperature, humidity, genetics, parental care, environmental factors, egg size and shape, predation, and incubation techniques, all play a role in the survival and reproductive success of bird populations.
Further research is needed to gain a deeper understanding of the complex interactions between these factors and their impacts on hatching time. This knowledge can inform conservation strategies and help protect bird species from threats such as pollution, habitat loss, and climate change.
Conservation efforts are essential for safeguarding bird populations and their hatching time. Protecting nesting sites, restoring habitats, reducing pollution, and implementing artificial incubation techniques are all important steps in ensuring the survival of bird species. By prioritizing the conservation of birds and their hatching time, we can contribute to the preservation of biodiversity and the health of our ecosystems.
Also Checkout: Are Birds Endothermic